World Heritage Sites in the United Kingdom
This is the fourth installment in which we bring these world treasures to our readers country by country. See the March-April issue for the World Heritage Sites in the United States, the May-June issue for those in Mexico, and the July-August issue for those in Canada. Each of the hyperlinks will take you to more information.
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) World Heritage Sites are places of importance to cultural or natural heritage as described in the UNESCO World Heritage Convention, established in 1972. There are thirty-three World Heritage Sites in the United Kingdom and the British Overseas Territories. (There are three different types of properties possible: cultural, natural, and mixed.)
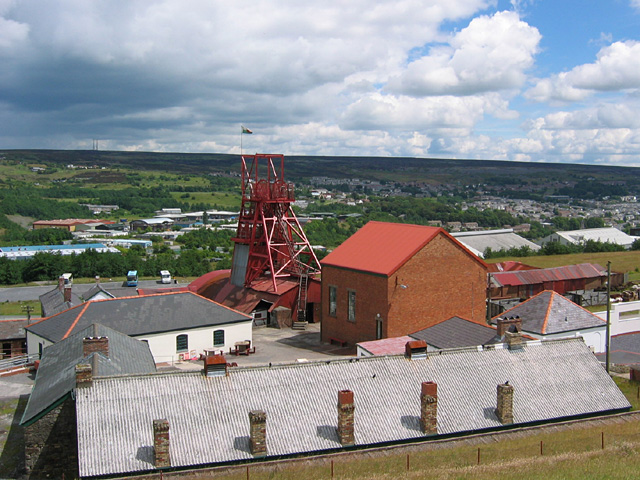

In the 19th century, Wales was the world’s foremost producer of iron and coal. Blaenavon Industrial Landscape is an example of the landscape created by the industrial processes associated with the production of these materials. The site includes quarries, public buildings, workers’ housing, and a railway
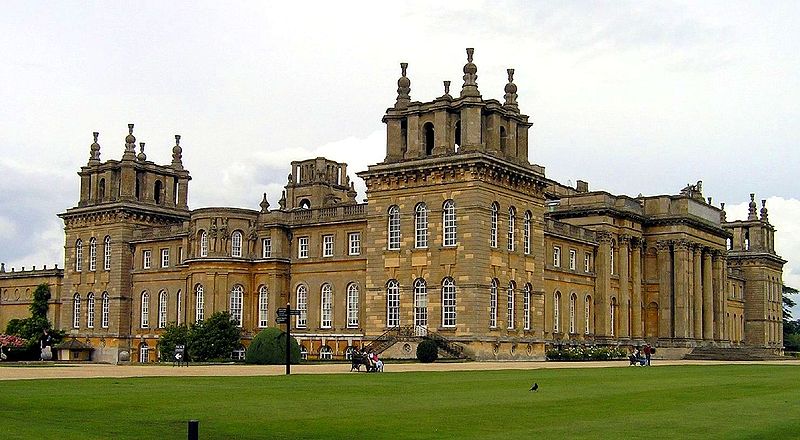

Blenheim Palace, the residence of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, was designed by architects John Vanbrugh and Nicholas Hawksmoor. The associated park was landscaped by Capability Brown. The palace celebrated victory over the French and is significant for establishing English Romantic Architecture as a separate entity from French Classical Architecture.
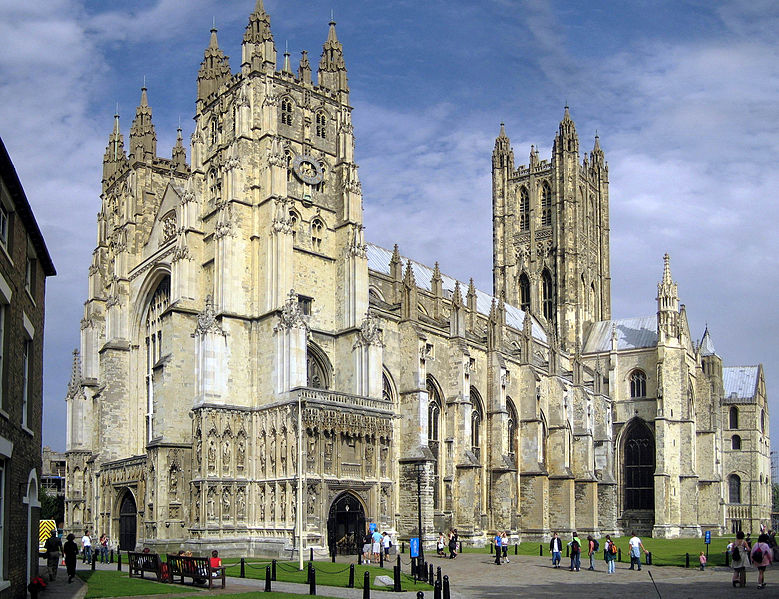

Canterbury Cathedral, St Augustine’s Abbey, and St Martin’s Church comprise the oldest church in England, dating back to the early stages of the introduction of Christianity to the Anglo-Saxons. The cathedral exhibits Romanesque and Gothic architecture, and is the seat of the Church of England.
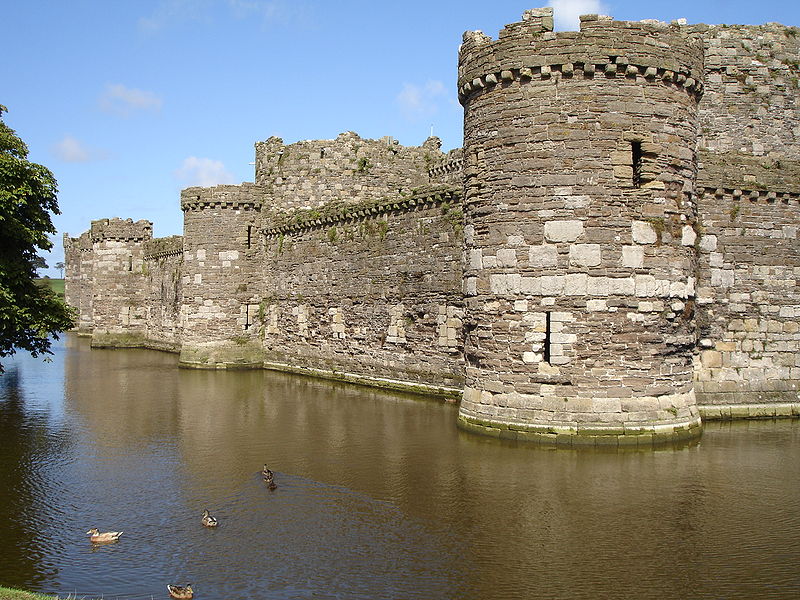

During the reign of Edward I of England (1272–1307), a series of castles was constructed in Wales with the purpose of subduing the population and establishing English colonies in Wales. The World Heritage Site covers many castles including Beaumaris, Caernarfon, Conwy, and Harlech. The castles of Edward I are considered the pinnacle of military architecture by military historians.
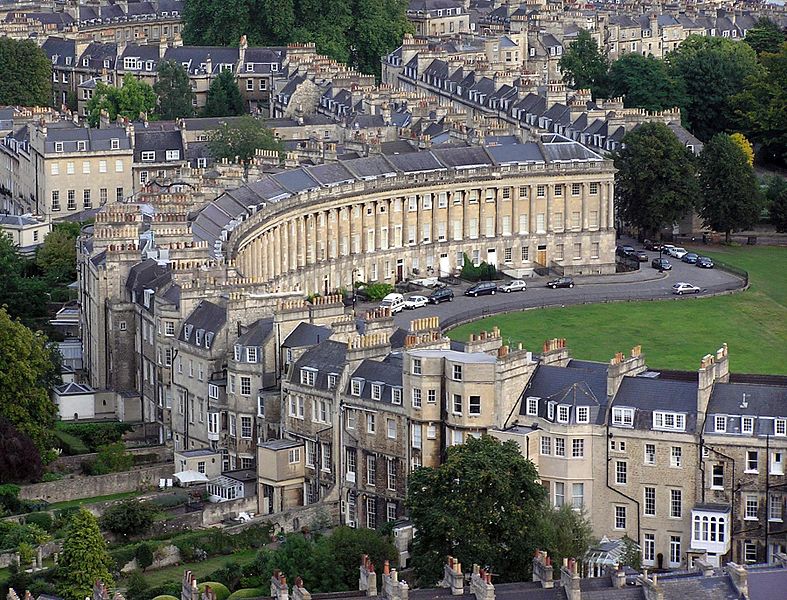

Founded by the Romans as a spa, an important center of the wool industry in the medieval period, and a spa town in the 18th century, the City of Bath has a varied history. The city is preserved for its Roman remains and Palladian architecture.
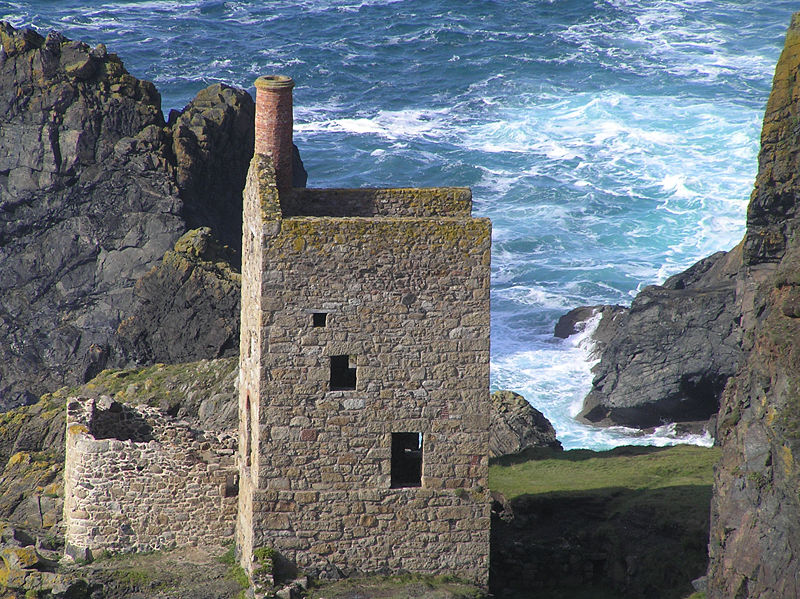

Tin and copper mining in the Cornwall and West Devon Mining Landscape boomed in the 18th and 19th centuries, and at its peak the area produced two-thirds of the world’s copper. The techniques and technology involved in deep mining developed here were used around the world.
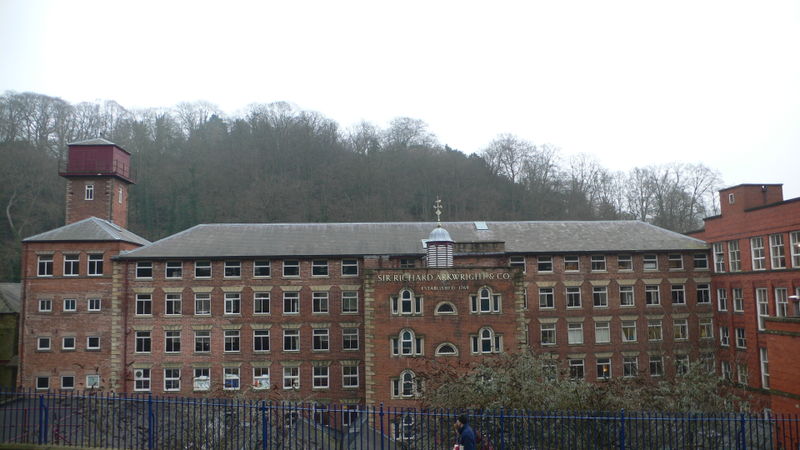

Derwent Valley Mills was the birthplace of the factory system. The innovations in the valley, including the development of workers’ housing and machines such as the water frame, were important in the Industrial Revolution.
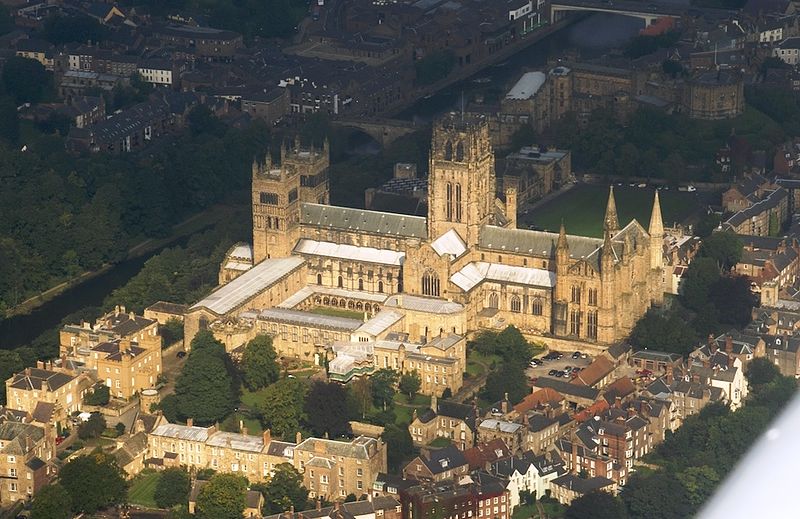

Durham Castle and Cathedral is the largest and finest example of Norman architecture in England and vaulting of the cathedral was part of the advent of Gothic architecture. The castle was the residence of the Durham prince-bishops.[

Famous for its scenic landscape of mountains, lakes, houses, gardens and parks, The English Lake District was celebrated through picturesque and romantic visual arts and literature from the 18th century on.
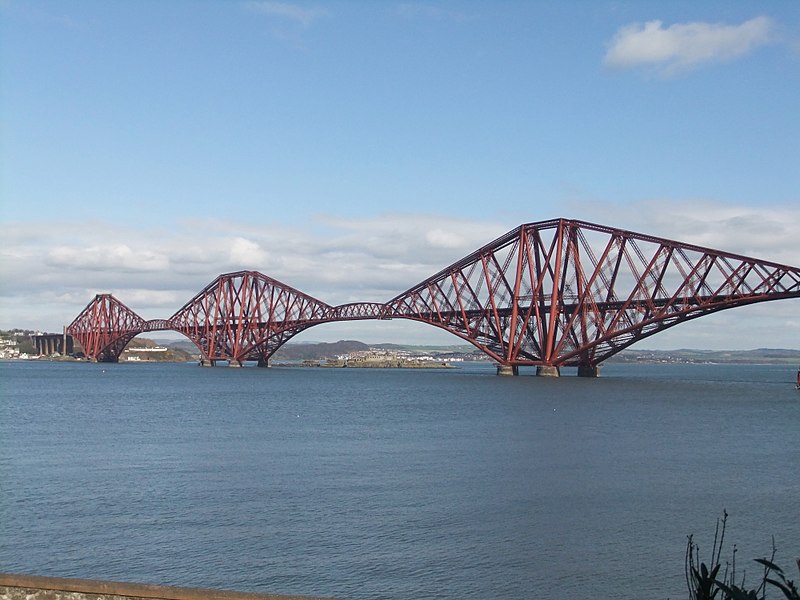

The Forth Bridge is a cantilever railway bridge 9 miles west of Edinburgh. It is considered an iconic structure and a symbol of Scotland. It was designed by the English engineers Sir John Fowler and Sir Benjamin Baker and built by Sir William Arrol of Glasgow who also built Tower Bridge in London.
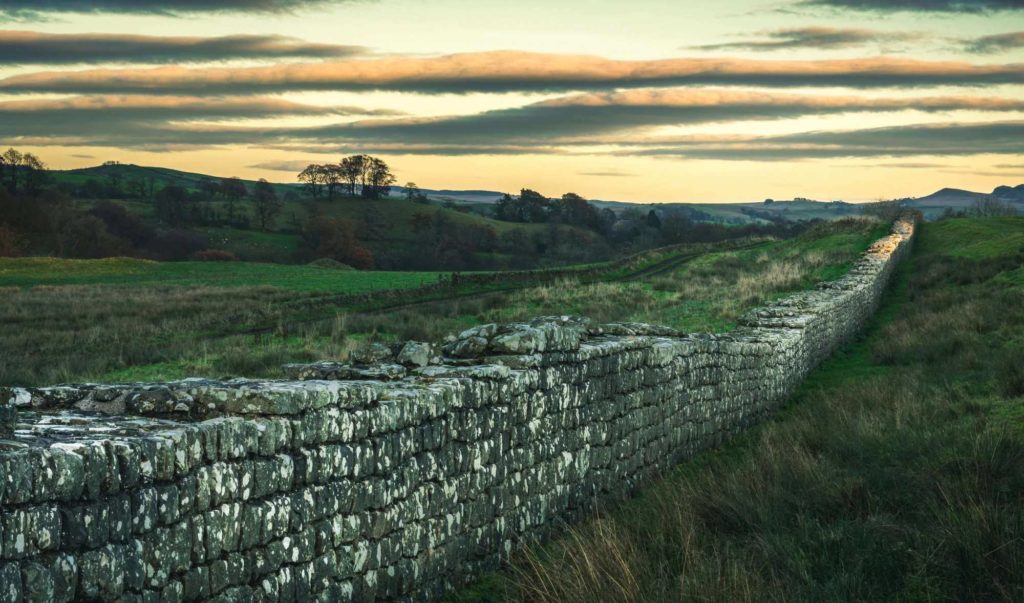

Called Frontiers of the Roman Empire, Hadrian’s Wall was built in 122 AD and the Antonine Wall was constructed in 142 AD to defend the Roman Empire from “barbarians”.
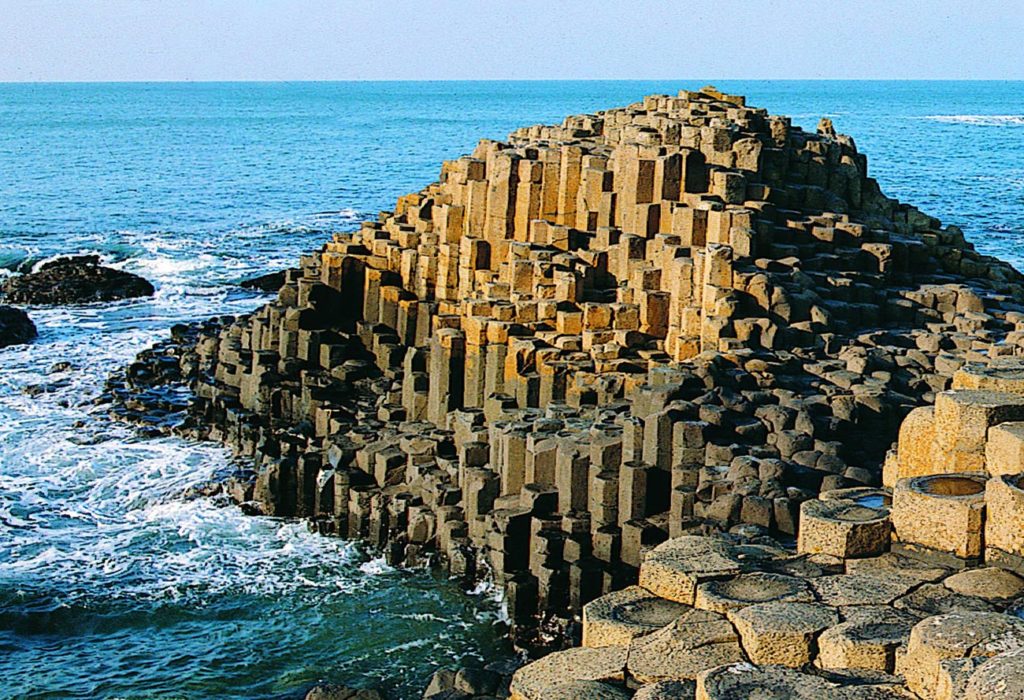

Giant’s Causeway and Causeway Coast is made up of 40,000 basalt columns projecting out of the sea. It was created by volcanic activity in the Tertiary period; it has been an inspiration for legends and has been the site of development in earth studies over the past 300 years.
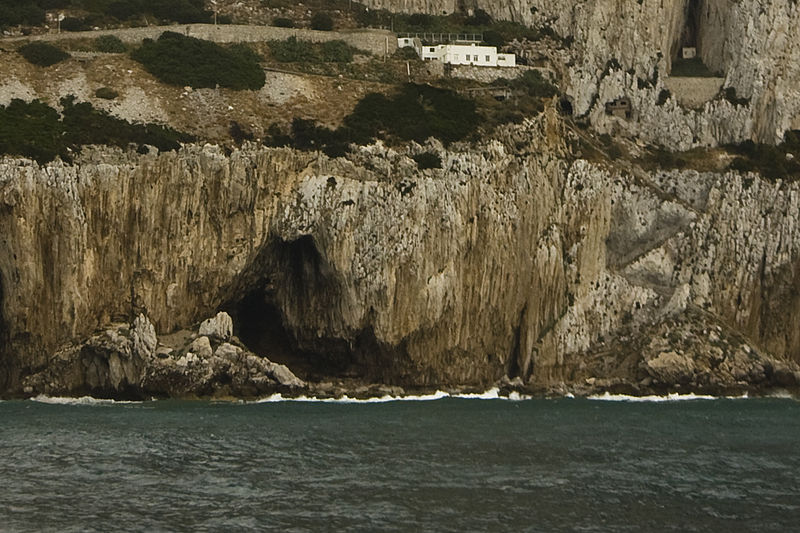

Comprising four natural sea caves, the Gorham’s Cave Complex is the last known site of Neanderthal inhabitation some 28,000 years ago. Evidences of occupation by modern humans are also present at the site.

Together, the Gough and Inaccessible Islands preserve an ecosystem almost untouched by mankind, with many endemic species of plants and animals.
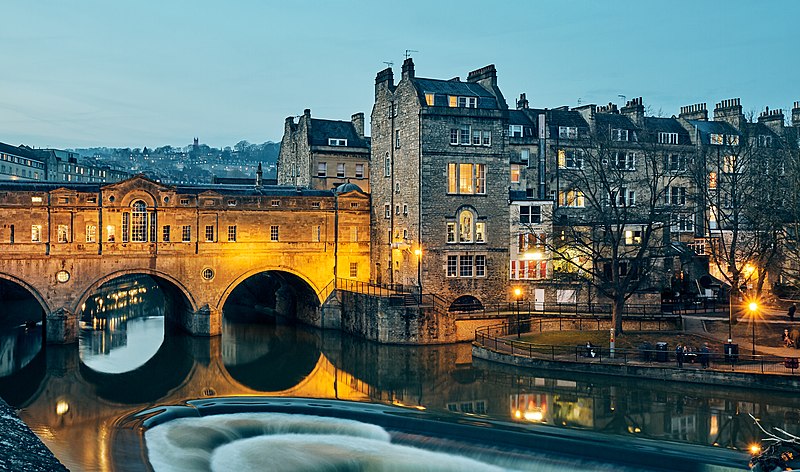

The Great Spas of Europe is a transnational heritage site, in England represented by Bath
and Somerset. A spa town is a resort based on a mineral spring. (The word spa is derived from the name of Spa, a town in Belgium.)
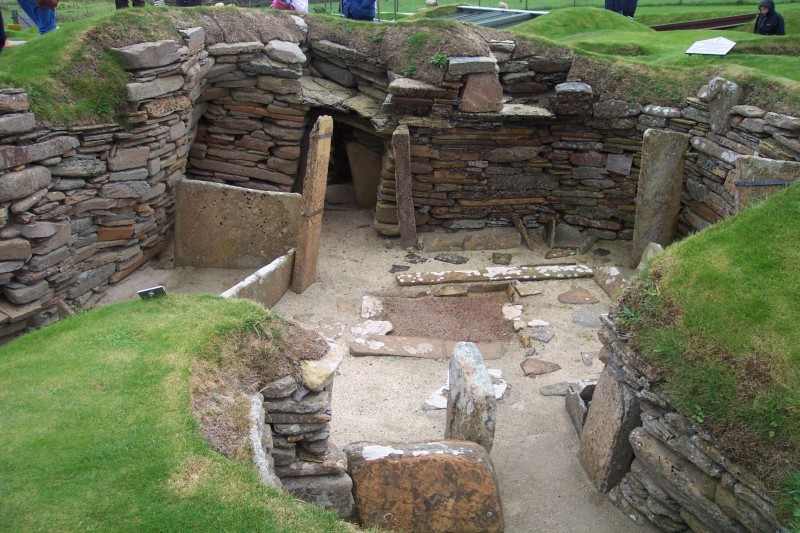

Heart of Neolithic Orkney refers to a group of Neolithic sites with purposes ranging from occupation to ceremony. It includes the settlement of Skara Brae, the chambered tomb of Maes Howe and the stone circles of Stenness and Brodgar.
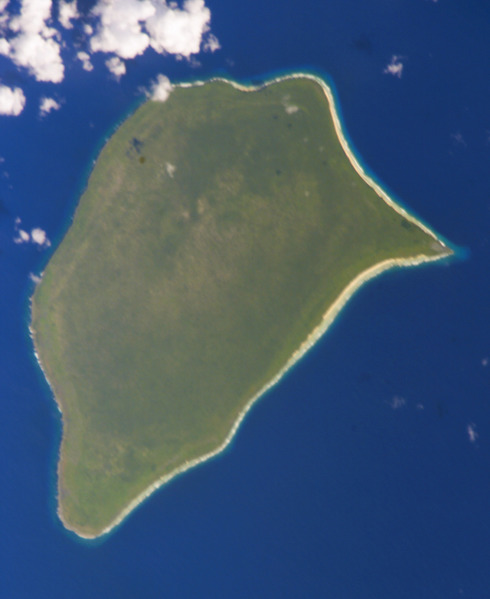

Henderson Island is an atoll in the south of the Pacific Ocean, the ecology of which has been almost untouched by man and its isolation illustrates the dynamics of evolution. There are ten plant and four animal species endemic to the island.
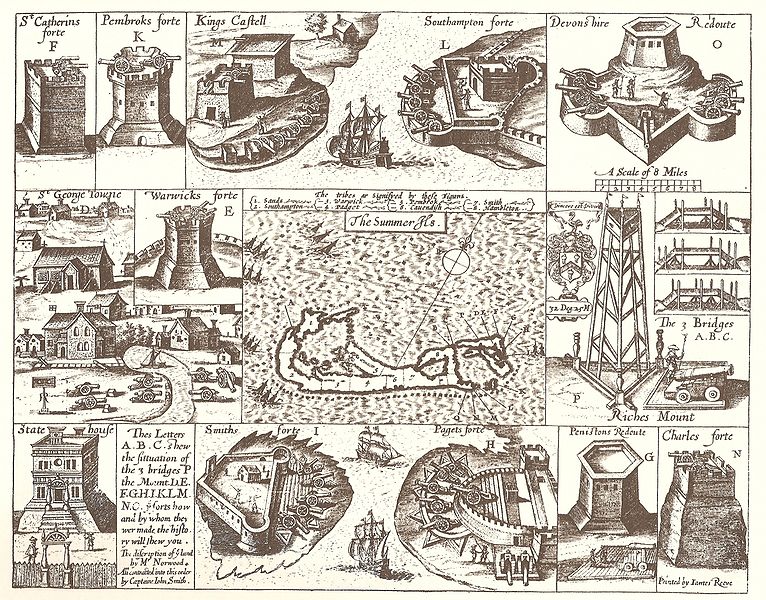
Founded in 1612, the Historic Town of St George and Related Fortifications, Bermuda is the oldest English town in the New World and an example of planned urban settlements established in the New World in the 17th century by colonial powers.
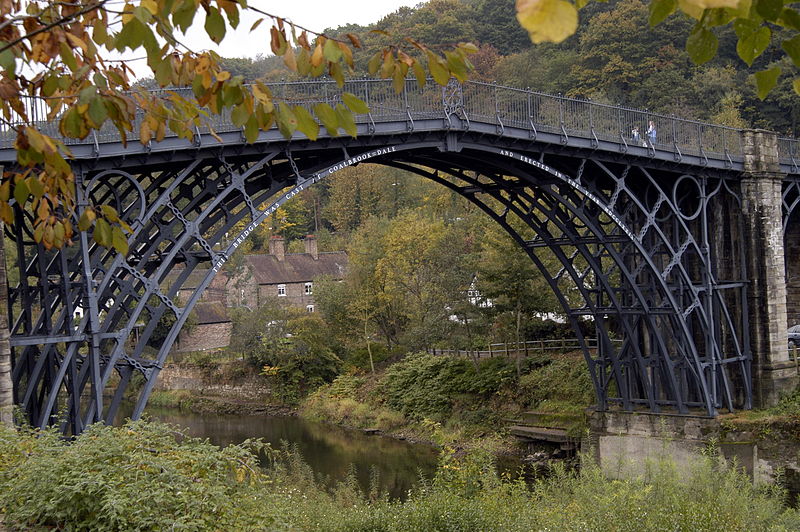

Ironbridge Gorge contains mines, factories, workers’ housing, and the transport infrastructure that was created in the gorge during the Industrial Revolution. The development of coke production in the area helped start the Industrial Revolution. The Iron Bridge was the world’s first bridge built from iron and was architecturally and technologically influential.
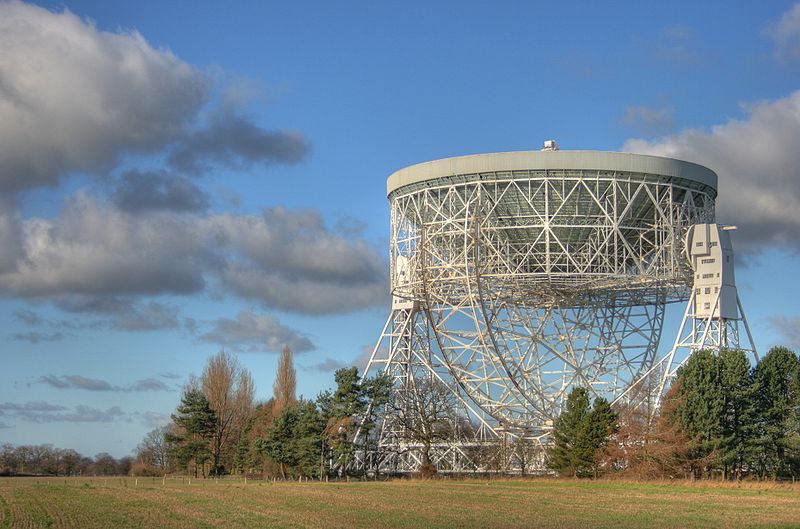

Jodrell Bank Observatory is one of the world’s leading radio astronomy observatories. Still in operation, it has had substantial scientific impact in fields such as the study of meteors and the moon, the discovery of quasars, quantum optics, and the tracking of spacecraft.
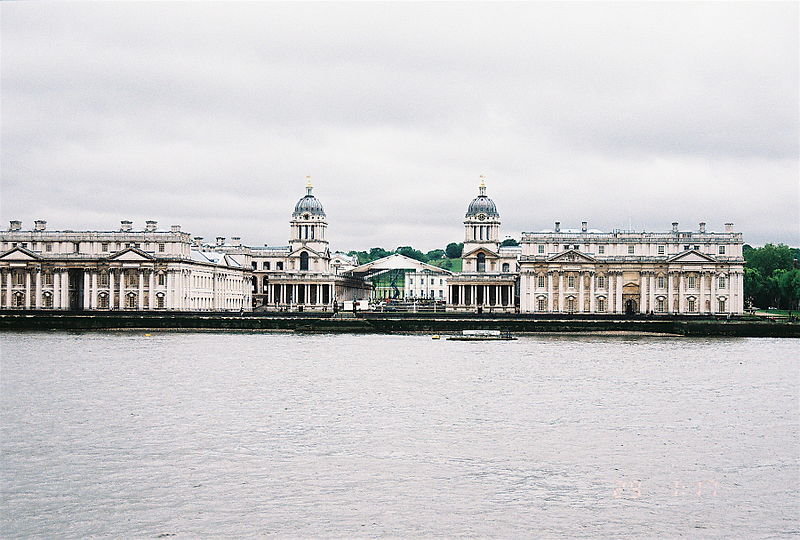

As well as the presence of the first example of Palladian architecture in England, and works by Christopher Wren and Inigo Jones, Maritime Greenwich is significant for the Royal Observatory where the understanding of astronomy and navigation were developed.
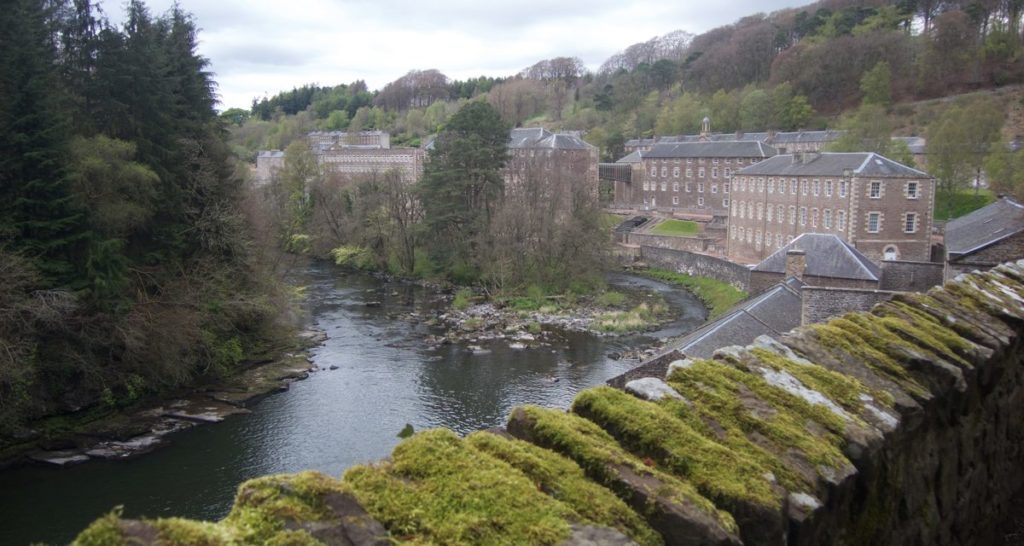

The community of New Lanark was created to provide housing for workers at the mills. Philanthropist Robert Owen bought the site and turned it into a model community, providing public facilities, education, and supporting factory reform.
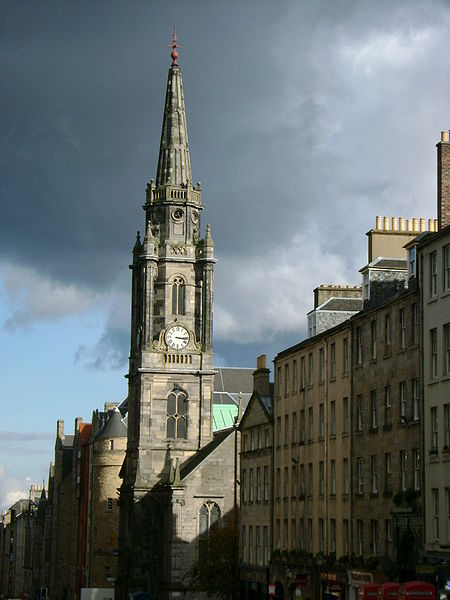

The Old Town of Edinburgh was founded in the Middle Ages, and the New Town was developed in 1767–1890. It contrasts the layout of settlements in the medieval and modern periods. The layout and architecture of the new town influenced European urban design in the 18th and 19th centuries.
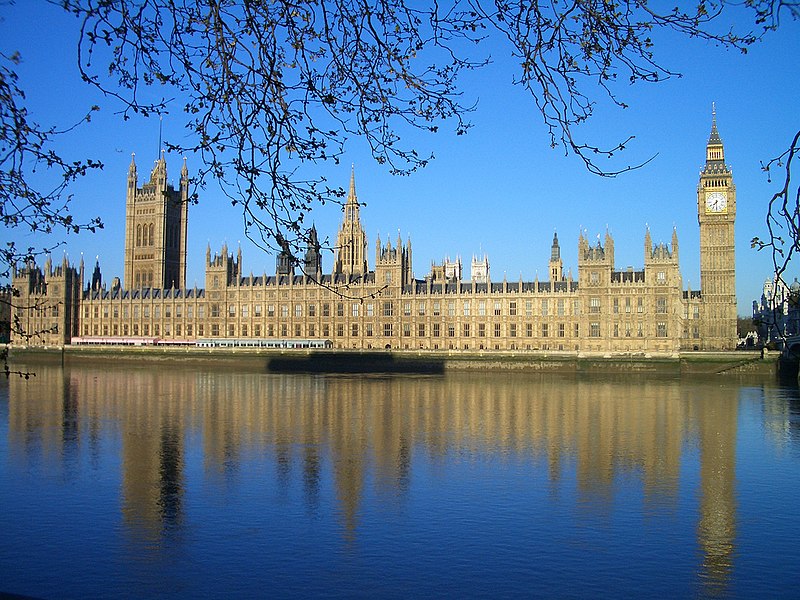

The Palace of Westminster and Westminster Abbey including Saint Margaret’s Church have been involved in the administration of England since the 11th century, and later the United Kingdom. Since the coronation of William the Conqueror, all English and British monarchs have been crowned at Westminster Abbey. Westminster Palace, home to the British Parliament, is an example of Gothic Revival architecture; St Margaret’s Church is the palace’s parish church, and although it pre-dates the palace and was built in the 11th century, it has been rebuilt.
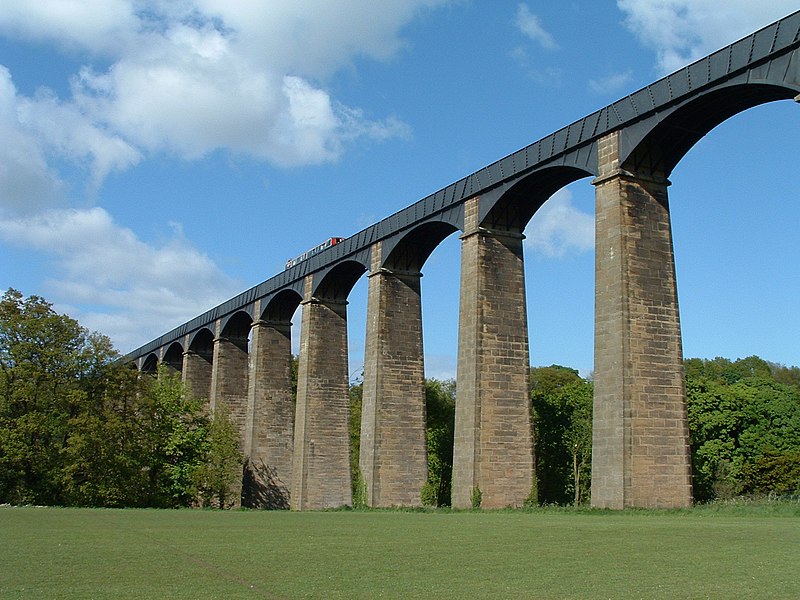

The Pontcysyllte Aqueduct and Canal was completed during the Industrial Revolution. It made innovative use of cast and wrought iron, influencing civil engineering across the world.
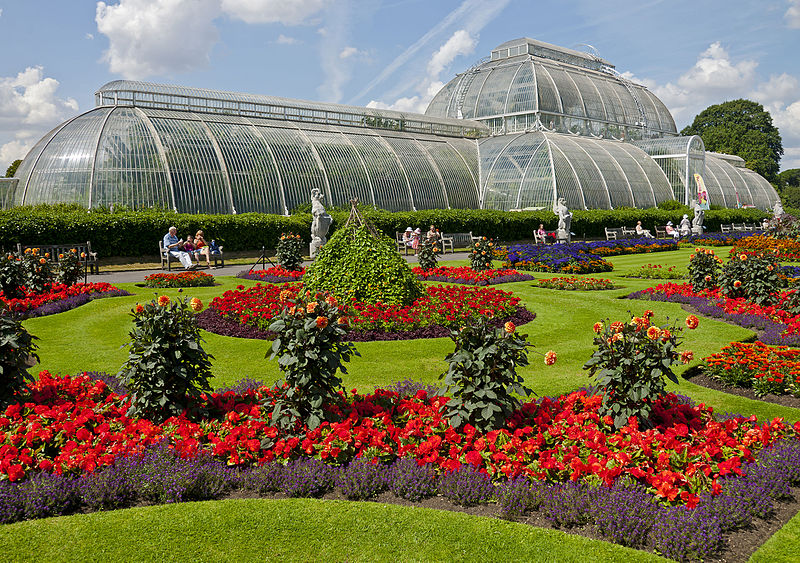

Created in 1759, the influential Royal Botanic Gardens (Kew Gardens) were used to study botany and ecology and furthered the understanding of the subjects.
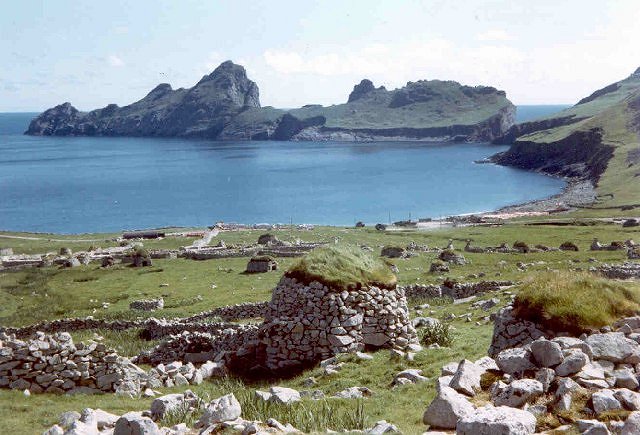

Although inhabited for over 2,000 years, the isolated archipelago of St Kilda has had no permanent residents since 1930. The islands’ human heritage includes various unique architectural features from the historic and prehistoric periods. It is also a breeding ground for many important seabird species.
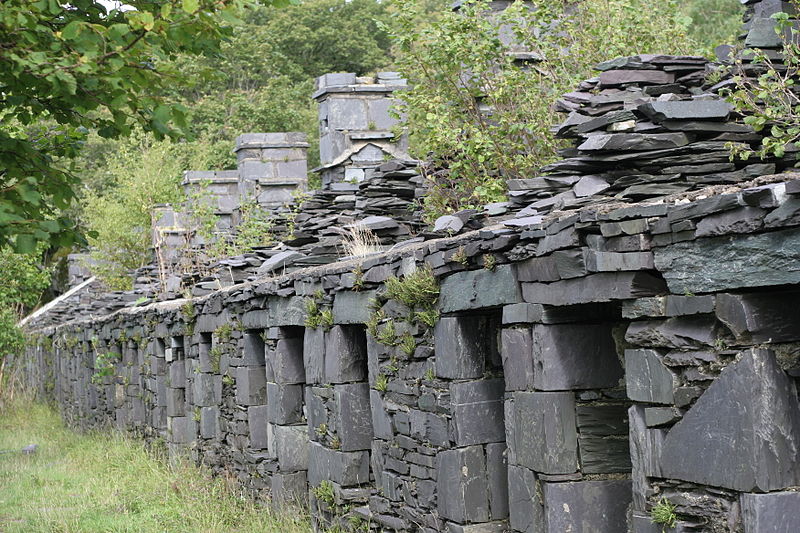

Saltaire was founded as a model village for workers. The site, which includes the Salts Mill, featured public buildings for the inhabitants and was an example of 19th-century paternalism.
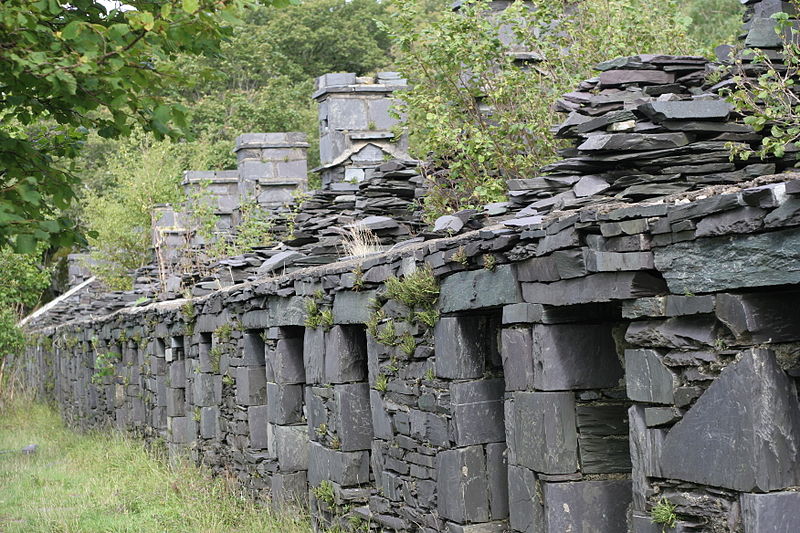

The Slate Landscape of Northwest Wales consist of six key areas, all located in Gwynedd, Wales.
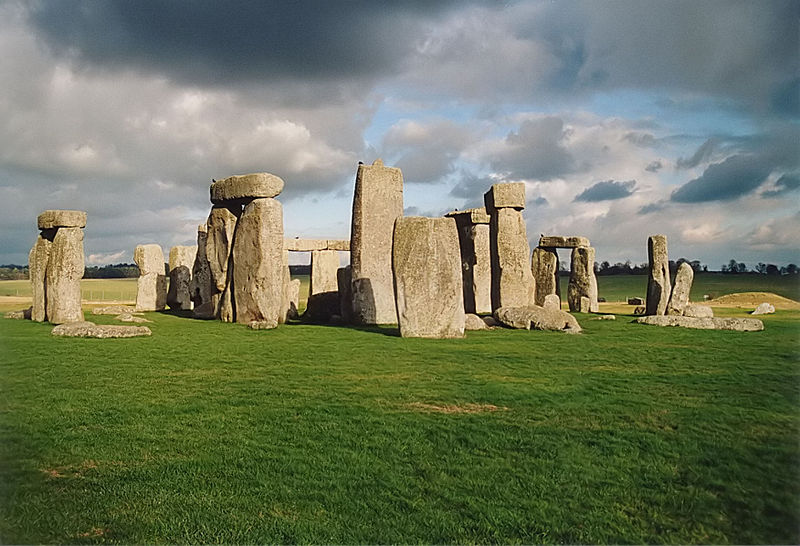

The Neolithic Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites are among the largest and most famous megalithic monuments in the world. They relate to man’s interaction with his environment. The purpose of the henges has been a source of speculation, with suggestions ranging from ceremonial to interpreting the cosmos.
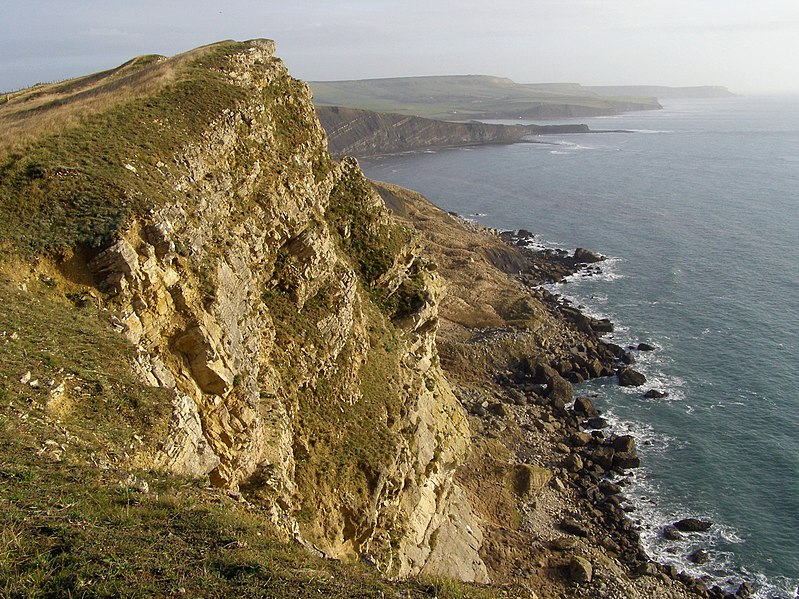

The cliffs that make up the Dorset and East Devon Coast are an important site for fossils and provide a continuous record of life on land and in the sea in the area since 185 million years ago.
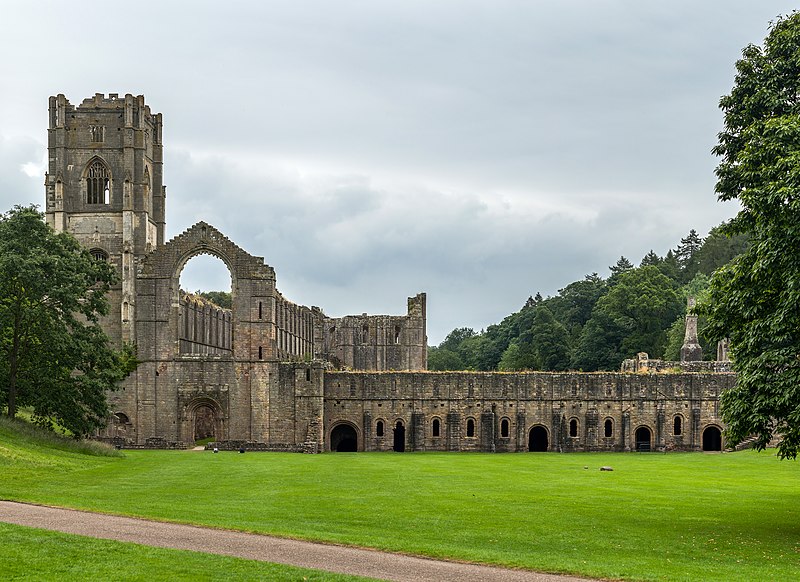

Studley Royal Park including the Ruins of Fountains Abbey: Before the mid-16th century, Fountains Abbey was one of the largest and richest Cistercian abbeys in Britain and is one of only a few that survives from the 12th century. The later garden, which incorporates the abbey, survives to a large extent in its original design and influenced garden design in Europe
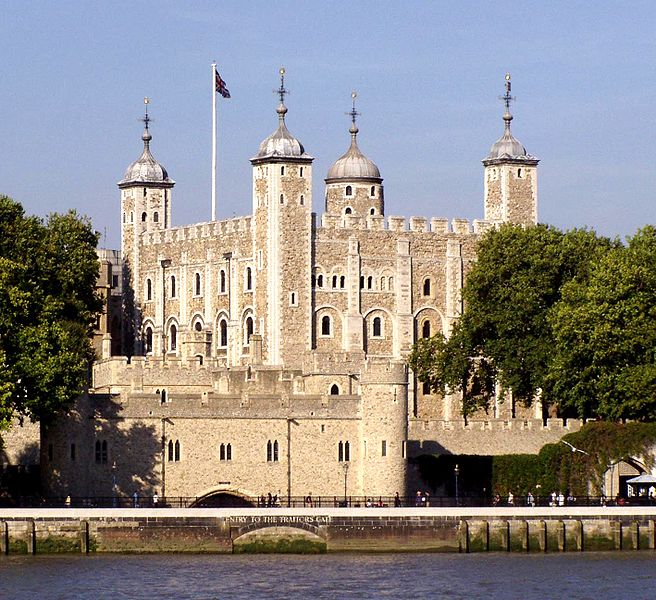

Begun by William the Conqueror in 1066 during the Norman conquest of England, the Tower of London is a symbol of power and an example of Norman military architecture that spread across England. Additions by Henry III and Edward I in the 13th century made the castle one of the most influential buildings of its kind in England.